reshoring
What is reshoring?
Reshoring is the process of bringing back manufacturing or production operations to their country of origin or a nearby region. It is a response to globalization, which led to the outsourcing and offshoring of manufacturing in the past, and represents a shift toward reestablishing and retaining production capabilities locally.
History and evolution of reshoring
The rise of offshoring in the late 20th century saw many businesses in North America and Western Europe shift their manufacturing operations to countries with lower operating expenses, largely in the Global South. Factors such as cheaper labor, reduced regulations and access to new markets fueled this trend.
However, as time passed, businesses experienced some challenges with offshoring. Quality control issues, longer lead times, intellectual property concerns and hidden costs gradually shifted interest in reshoring.
The reasoning behind reshoring
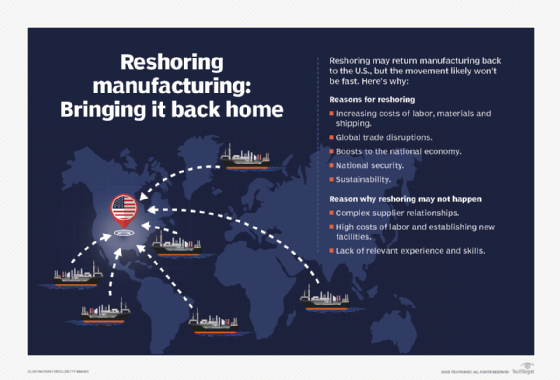
Several factors have contributed to the momentum behind reshoring:
- Cost considerations. The cost dynamics of offshoring have changed significantly over the years. Wage gaps between countries have narrowed, transportation costs have increased, and factors such as rising fuel prices and currency fluctuations have made offshore manufacturing less cost-effective.
- Quality control and intellectual property protection. With local manufacturing, companies have better control over product quality, consistency and compliance. Moreover, protecting intellectual property becomes easier within their own country's legal frameworks.
- Supply chain resilience. Global disruptions, such as the COVID-19 pandemic, exposed vulnerabilities in long and complex supply chains. Reshoring allows for shorter supply chains, reducing the risk of disruptions and ensuring faster response times during crises.
- Flexibility and agility. Local manufacturing lets companies act with greater agility, quickly responding to market demands, customizing products for specific regions and innovating in a fast-changing business environment.
- Sustainability and environmental impact. The growing focus on reducing carbon footprints has highlighted the environmental impact of long-haul transportation. Reshoring allows for more sustainable practices and reduces the ecological strain caused by transportation.
Challenges and considerations for reshoring
While reshoring offers numerous advantages, some challenges and considerations need to be addressed:
- Workforce implications. Reshoring requires a skilled workforce, often necessitating investment in training and development programs.
- Infrastructure assessment. The availability of suitable infrastructure, including factories, transportation networks and utilities, must be evaluated before transitioning manufacturing operations.
- Policy and regulatory factors. Governments can play a crucial role in incentivizing reshoring through favorable policies, trade agreements and tax incentives. Understanding the regulatory landscape is essential for successful reshoring initiatives.
- Transitioning from offshore to onshore. Shifting production back to the home country or a nearby region requires careful planning, including logistics, supply chain migration and managing potential disruptions during this transition phase.
Future trends and outlook for reshoring
The future of reshoring will be shaped by several key trends.
First, technological advancements will play a significant role in driving further reshoring efforts. Innovations such as automation, artificial intelligence and advanced robotics are expected to reduce the significance of labor cost differentials, making reshoring more viable and competitive.
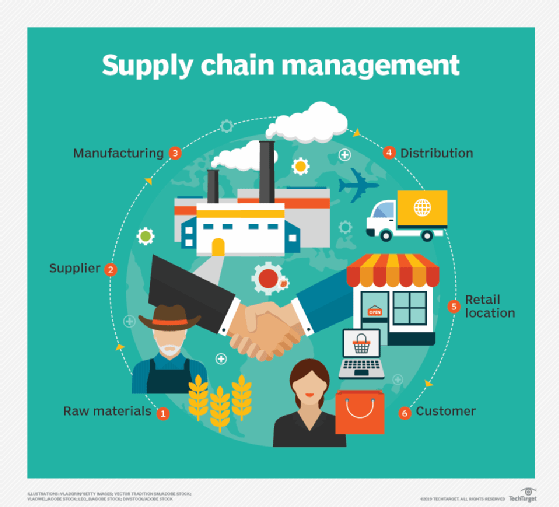
In addition to technological advancements, there will be a noticeable shift from a globalized supply chain to a more regionalized and localized model. This transition aims to reduce dependency on long and complex supply chains, thereby enhancing overall supply chain resilience.
By bringing manufacturing operations closer to the end markets, companies can achieve faster response times, improved customization and greater agility in meeting local market demands.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on sustainability within the manufacturing industry. As concerns about climate change and environmental impact continue to rise, companies are increasingly prioritizing sustainable practices.
This focus on sustainability will drive reshoring initiatives as companies seek to reduce their carbon footprint and adopt environmentally friendly manufacturing processes that adhere to local regulations and standards.
Why reshoring presents an opportunity
Reshoring presents a strategic opportunity for businesses to bring manufacturing operations back to their home country or a nearby region. The evolving cost dynamics, risk mitigation, technological advances, increased control over quality and agility in responding to market demands are some of the key drivers behind reshoring.
While challenges exist, careful consideration of workforce, infrastructure, policies and the transition process can lead to successful reshoring initiatives.
Reshoring will continue to shape the global manufacturing landscape, helping companies build more resilient, sustainable and competitive operations.
Learn how reshoring manufacturing to the U.S. is on the rise. It is being driven by supply chain risks, sustainability demands, and policy incentives. Explore why digital tech tops supply chain trends.






