SIPOC (suppliers, inputs, process, outputs, customers) diagram
What is a SIPOC (suppliers, inputs, process, outputs, customers) diagram?
A SIPOC (suppliers, inputs, process, outputs, customers) diagram is a visual tool for documenting a business process from beginning to end prior to implementation. SIPOC -- pronounced sigh-pock -- diagrams are also referred to as high-level process maps because they do not contain much detail.
SIPOC diagrams are useful for focusing a discussion, helping team members agree on a common language and understanding a process for continuous improvement.
In Six Sigma, SIPOC is often used during the define phase of the DMAIC (define, measure, analyze, improve, control) methodology. Some organizations use SIPOC diagrams in the opposite direction, or COPIS, to map the value of the customer to a business process.
How to create a SIPOC diagram
SIPOC diagrams are tables that document the inputs and outputs of a process. They can be created by following seven steps:
- Choose a process. The first step is to choose a business process that would benefit from charting in a SIPOC diagram. A team can then be assembled around the key players of that process.
- Define the process. The diagram starts with the P section, which is usually an overview of the business process in four to five high-level steps that each consist of an action and a subject. This could include the starting and ending points for the process or a simple flow chart.
- Identify the outputs. This section includes three to four outputs with little supporting information, typically neutral in tone and using nouns only. Inputs and outputs can be anything ranging from materials and products to services or information.
- Identify the customers. These are the individuals who will receive the outputs or will benefit from the process. Customers are not always external consumers and could be co-workers, board members or other internal stakeholders.
- Identify the inputs. This section includes the resources that are necessary for the process to function properly. Similar to outputs, only the important, overarching inputs should be listed.
- Identify the suppliers. This section lists the suppliers associated with each of the inputs that the process requires. A supplier is anyone who has a direct effect on the outputs.
- Share the diagram. Once the diagram is complete, it should be shared with any relevant stakeholders and validated before moving along with the process.
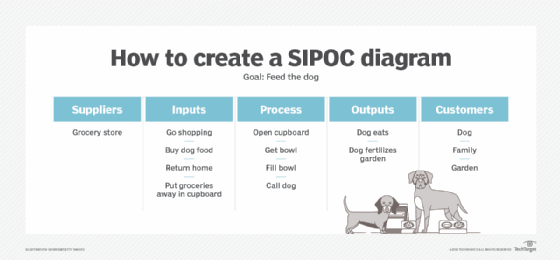
Here is an example of how a continuous improvement team might use a SIPOC diagram for a simple process, such as feeding the family dog. The diagram can be created rather quickly by drawing a chart with five columns. Each column is labeled, from left to right, with the letters S-I-P-O-C or the words suppliers, inputs, processes, outputs and customers.
When to use a SIPOC diagram
Creating a SIPOC diagram can be beneficial in a variety of applications, the most popular being for continuous improvement. Since a finished SIPOC diagram provides a high-level map of a process, it can be used for identifying problem areas, conducting process analysis and explaining business operations to an audience.
In addition, a SIPOC diagram can be helpful when parts of a process are unclear. It forces team members to identify and centralize information such as supplier contacts, project specifications and target customers.
Benefits of a SIPOC diagram
A few benefits of using a SIPOC diagram include the following:
- Increases transparency across an organization.
- Provides an overview of a project for stakeholders.
- Can be used as a training tool for newer employees.
- Helps with problem-solving initiatives.
- Creates a reusable template for various processes and projects.
- Ensures all team members are on the same page.







